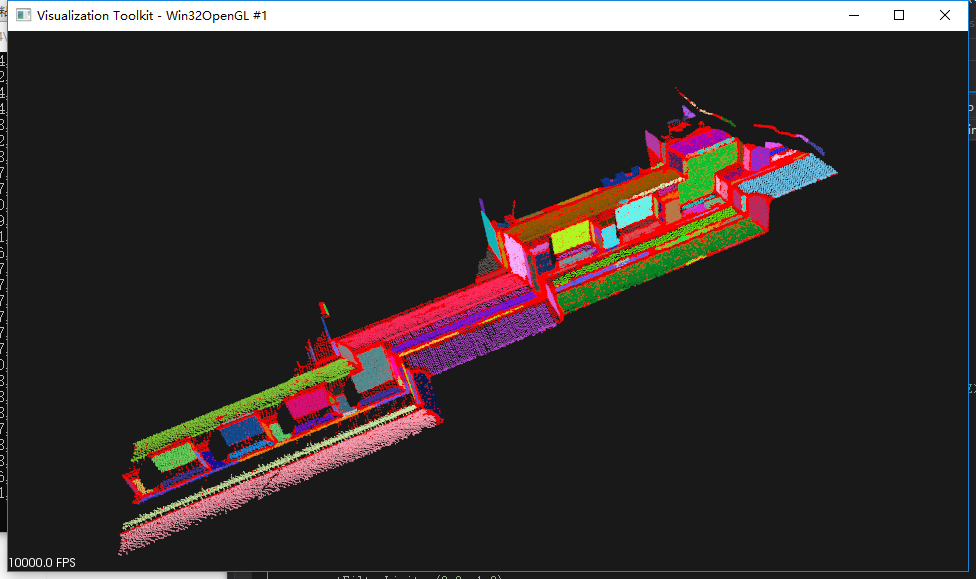
1.原理: 区域生长法:
通过曲率 和法向量的夹角 作为阈值来分割点云,同一区域内的点云趋于同一平面上,曲率不大,对比于欧式聚类分割法,区域生长法可以分割出曲率不连续(即曲率变换较大)但点云连续的区域 。
步骤:
PCL中的类pcl::RegionGrowing用来实现点云的区域生长分割。区域生长分割是基于点云法线的分割算法,算法的主要思路如下:
点云中有未标记点,按照点的曲率值对点进行排序,找到最小曲率值点,并把它添加到种子点集;
对于每个种子点,算法都会发现周边的所有近邻点。
1)计算每个近邻点与当前种子点的法线角度差(reg.setSmoothnessThreshold),如果差值小于设置的阈值,则该近邻点被重点考虑,进行第二步测试;
2)该近邻点通过了法线角度差检验,如果它的曲率小于我们设定的阈值(reg.setCurvatureThreshold),这个点就被添加到种子点集,即属于当前平面。
通过两次检验的点,被从原始点云去除。
设置最小点簇的点数min(reg.setMinClusterSize),最大点簇为max(reg.setMaxClusterSize)。
重复1-3步,算法会生成点数在min和max的所有平面,并对不同平面标记不同颜色加以区分。
直到算法在剩余点中生成的点簇不能满足min,算法停止工作。
2.在PCL中: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/search/search.h> #include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/region_growing.h> int main (int argc, char ** argv) { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>) ; if ( pcl::io::loadPCDFile <pcl::PointXYZ> ("region_growing_tutorial.pcd" , *cloud) == -1 ) { std ::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std ::endl ; return (-1 ); } pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree = boost::shared_ptr <pcl::search::Search<pcl::PointXYZ> > (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud <pcl::Normal>) ; pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> normal_estimator; normal_estimator.setSearchMethod (tree); normal_estimator.setInputCloud (cloud); normal_estimator.setKSearch (50 ); normal_estimator.compute (*normals); pcl::IndicesPtr indices (new std ::vector <int >) ; pcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass; pass.setInputCloud (cloud); pass.setFilterFieldName ("z" ); pass.setFilterLimits (0.0 , 1.0 ); pass.filter (*indices); pcl::RegionGrowing<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> reg; reg.setMinClusterSize (50 ); reg.setMaxClusterSize (1000000 ); reg.setSearchMethod (tree); reg.setNumberOfNeighbours (30 ); reg.setInputCloud (cloud); reg.setInputNormals (normals); reg.setSmoothnessThreshold (3.0 / 180.0 * M_PI); reg.setCurvatureThreshold (1.0 ); std ::vector <pcl::PointIndices> clusters; reg.extract (clusters); std ::cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size () << std ::endl ; std ::cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0 ].indices.size () << " points." << endl ; std ::cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" << std ::endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << std ::endl ; int counter = 0 ; while (counter < clusters[0 ].indices.size ()) { std ::cout << clusters[0 ].indices[counter] << ", " ; counter++; if (counter % 10 == 0 ) std ::cout << std ::endl ; } std ::cout << std ::endl ; pcl::PointCloud <pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud (); pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer ("Cluster viewer" ) ; viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud); while (!viewer.wasStopped ()) { } return (0 ); }